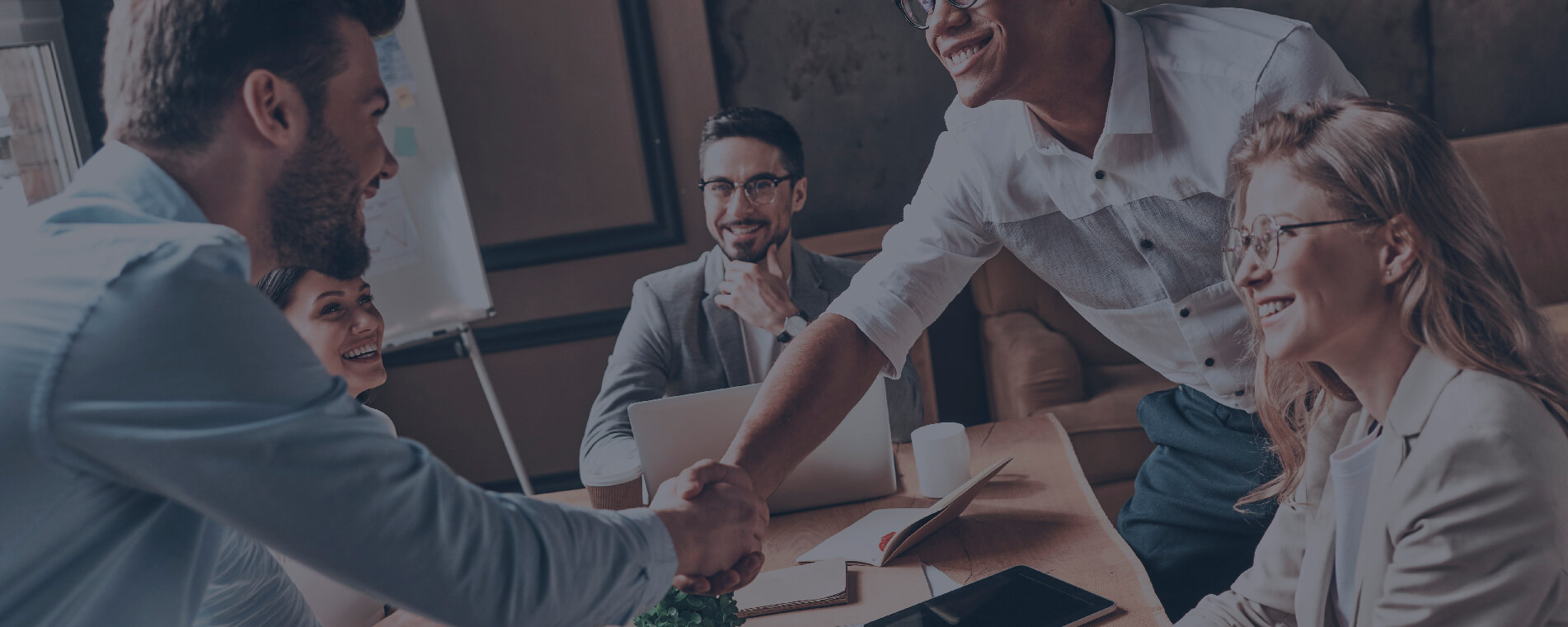

“What differentiates us from others is that we are a manufacturer of certification technology. In other words, we not only issue digital certificates, we protect them and offer solutions so that our clients can use them as usual”. This is how Jaime Castelló, CEO of Ivnosys, explains the company’s business card, which has seen the demand for its services increase both because of the pandemic (240% in the first quarter of last year) and because of the increase in cyber-attacks and the need for companies to avoid fraud.
“We have to emphasise security”, insists Castelló, “in protecting our digital identity because that is what guarantees the other person, the person facing us, who we are”, a key aspect in times of pandemic, when many of the operations, for example with the Administration, are done ‘online’. In this sense, Ivnosys acts as a guardian, as its digital certificates “cannot be transferred, that is, the client gives an authorisation for use and it is deposited in Ivnosys”. In this way, all transactions are recorded and audited.

Specialised in the development of software to centralise, protect and manage the digital identity and electronic transactions of companies with the maximum legal guarantees, Ivnosys currently has a team of 120 professionals and is the company in which the Ibex-35 trusts to protect its data.
Our technology also allows companies to reduce the use of paper by up to 100% through the implementation of electronic signature, certification and notification solutions, which also translates into cost savings of between one and three million euros per month.
More and more companies and professionals are being required by the regulatory authorities to use a qualified digital certificate for their electronic communications and procedures. We find the example in different regulations such as the European eIDAS regulation, Law 6/2020 and Law 39/2015, which require the use of a qualified digital certificate.
But how do I know if I am working with a qualified digital certificate? What does this qualification mean? We tell you in the following post.
A qualified digital certificate is issued through a Qualified Signature Creation Device (QSCD) by a Qualified Trust Service Provider.
The qualified certificate incorporates data that verify the identity of the owner and provide legal validity to the actions carried out with it. This is because it contains data such as:
The main difference between the qualified and unqualified certificate is that the qualified one is presumed to be legally valid. Thus, if the qualified certificate is used for a qualified signature, it serves as indisputable proof in the event of legal proceedings, so that:
In accordance with the eIDAS Regulation regarding electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions, the electronic signature certificate links the validation data of a signature with a natural person.
The most secure signature is the qualified signature, in other words, the signature made with a digital certificate. For this, it is necessary that the digital certificate is qualified and complies with the requirements mentioned above.
The recognition of qualified signatures is set out in article 25 of the eIDAS regulation:
Article 25 – Legal effects of electronic signatures
You are probably familiar with it and you may have already had to use your digital certificate to access your employment history report, check your taxes or carry out any type of online procedure with the Public Administration.
But do you know exactly what a digital certificate is and what kind of procedures do you need it for?
We can understand the digital certificate as an electronic ID that identifies us digitally and allows us to carry out transactions on the Internet. Depending on the task we need to carry out (signing a document, applying for a grant from the local council, etc.), we must use a specific type of certificate. In the case of companies, the most commonly used are the certificates of representation with the Public Administrations and the certificate of electronic signature.
Its use is becoming more and more widespread in companies, especially since the pandemic. Thus, more than 80% of users have carried out telematic procedures with the Public Administration, for which they needed a digital certificate. What is the reason for this increase in the use of digital certificates? Quite simply. Until now, when we needed to carry out a procedure with a public organisation, we used to go to the offices and show our ID card. In the same way that we showed our ID card in this process of physical identification, we have to use the digital certificate to do it electronically.
Since the pandemic, more than 80% of users have carried out telematic procedures in the Public Administration, for which they needed a digital certificate.
With the digital certificate we can access private and confidential information, which is really important in the case of companies. If a person had the digital certificate representing a company in their hands, they could access tax data and carry out transactions unknowingly on behalf of the company.
The increase of electronic transactions through the use of digital certificates and electronic signatures has led to their regulation with Law 6/2020, on electronic trust services, which is an adaptation of the European eIDAS regulation.
Among the points dealt with, Law 6/2020 recognises a validity period of 5 years for digital certificates and the possibility of renewing them only once to guarantee maximum security.
>> We recommend: eIDAS Regulation: the security of electronic signatures
To work online securely, it is necessary to use a qualified digital certificate, which means a certificate issued by a Certification Authority. This is the case of organisations such as the FNMT, Camerfirma or Ivnosys.
A qualified digital certificate, also known as a “qualified certificate of electronic signature”, is a digital certificate generated by a secure signature creation device known as QSCD (Qualified Signature Creation Device) and which has been issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider, such as Ivnosys.
This entity issues the certificates and grants legal validity to all uses made with them. In addition, there are tools such as IvSign that are committed to greater security control.
Many companies install digital certificates on employees’ computers, which means:
However, with IvSign it is possible to stop all these situations as the certificates are issued from the platform itself and stored directly in the cloud. Thanks to this, employees can use them from any device and the company can assign their use, controlling in real time who uses them and when, thanks to the auditing process incorporated in the platform.
Among the most frequent uses that companies make with the digital certificate is the management of electronic procedures with the Public Administration. This is due to the obligatory compliance of companies and professionals with Law 39/2015. This regulation only allows procedures to be carried out by electronic communication, which affects the management of electronic notifications.
Thus, to consult notifications and carry out any task through websites of public administrations, it is necessary to be accredited with a digital certificate. Automating these procedures is also possible thanks to management platforms such as IvNeos.
Another principal use is electronic signatures. Paper signatures seem to be a thing of the past. Companies now use electronic methods to sign contracts or any type of document. Thus, it is much more convenient and agile to send a document by e-mail and receive it electronically signed. It is no longer necessary to wait for a customer or employee in person to complete formalities, and this greatly optimises the company’s resources, both in terms of time and money.
The electronic signature has many advantages for companies. Its use is usually applied between two signatories, for example, between the company and an employee, a supplier… Moreover, it is particularly useful when we need a document to be signed by several people.
Can there be several signatories, and are there tools that allow this to be done securely? We answer your questions in today’s post.
When we include several signatories in an electronic document we must ask ourselves the question: Are all signatures going to have the same legal value or should there be an order of signatures?
This order is important in those cases where we need certain people to have signed the document before it is made available to the rest of the signatories. For example, we may need the sales manager to validate an offer made by the sales team before it is sent to the customer.
Thus, there are two types of multiple signatures:
Using multiple signature requires a higher level of legal security because while in the simple signature we must ensure the validity of the signature made by a user, in the case of multiple signature we have to ensure the validity of several signatories.
This will require the use of digital tools prepared for this purpose, such as IvCert, which is developed by a Qualified Trust Service Provider. As an example, the PSCC acts as an electronic notary and provides legal support to the electronic signatures that are made through the platform.
Thus, the tool offers the two types of multiple signatures mentioned above. How to do it? We tell you the steps below.
The IvCert platform allows you to send documents for recipients to sign electronically. When configuring the electronic signature that we request for each signatory, we will define the type of signature, until when they can sign the document, add elements and a customizable message, and how the order of the signatures should be. Let’s see how to do this last point:
This option allows you to group signature operations so that they are completed in parallel, which means that signers can sign at any time without depending on each other. In the case of a grouping prior to other signature tasks, these will not start until all the operations included in the grouping are completed.
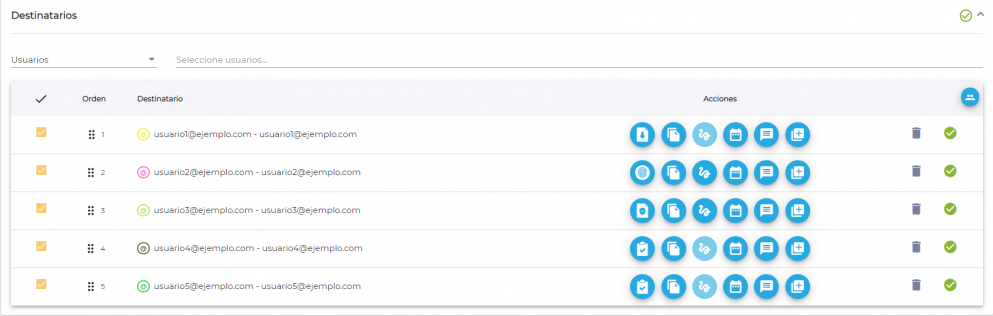
In this case the tool offers two options:
We will indicate the order of signers, so that signer 1 will be the first person to sign the document. Once he/she has done so, he/she will pass to signer 2, and so on consecutively.
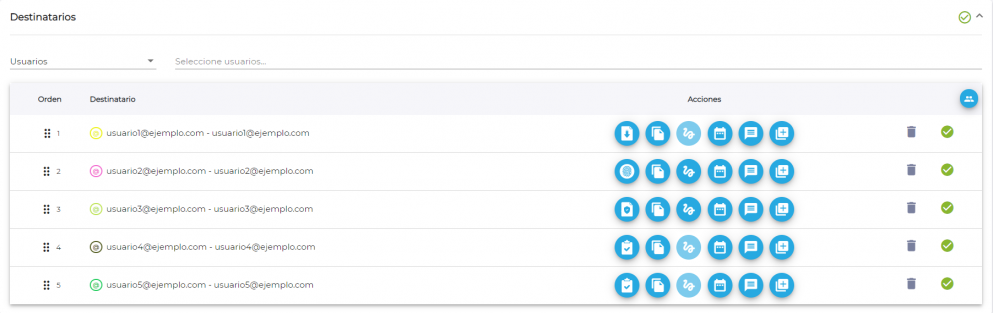
Select the users who should sign the document first. In this example, signers 1 and 2 must sign the document (regardless of who signs it first) so that it can be signed by the third person. Once this selection is applied, it is displayed as follows:
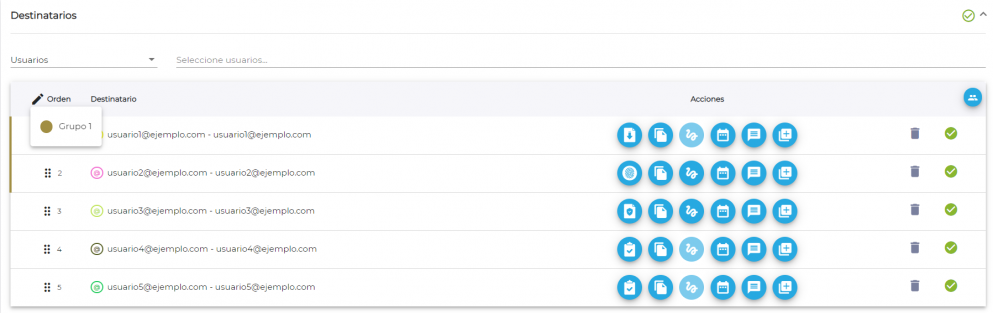
For example: using the following image as a reference, you can see that in the group task 1 and task 2 (regardless of which user is indicated) will be able to be completed simultaneously.
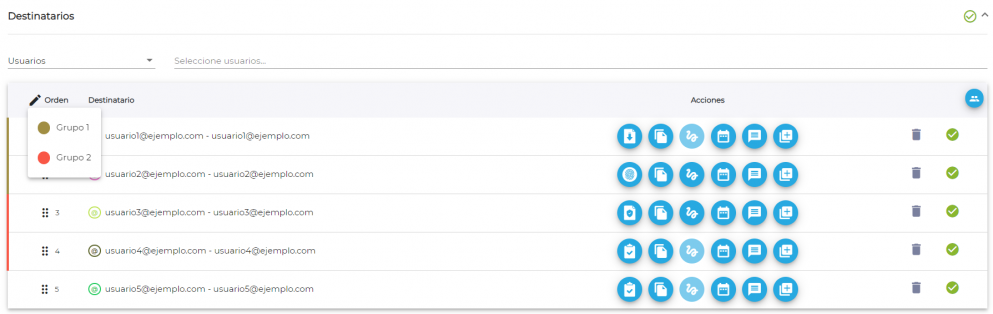
Note: we can make as many signature groups as we wish. In the following image we show 2 groups: a first group that includes signer 1 and 2, and a second group that includes signers 3 and 4. In this case, both groups should sign the document before moving on to the fifth person.
As we already know, a digital certificate is the electronic document that guarantees a person’s identity on the Internet and, depending on the type of digital certificate, allows them to carry out actions such as signing documents or accessing electronic offices. Therefore, nowadays, it is essential for companies and professionals to have a certificate in order to be able to carry out their work.
Remember that if you do not have a digital certificate, you must go to a Certification Authority, recognised as a Trusted Service Provider such as Ivnosys, to have it issued. It is important to do so with an officially recognised entity to ensure that the identity of the holder, the integrity of the message and the non-repudiation of electronic transactions are guaranteed.
There are many types of digital certificates, as they can identify us as a natural person (if we are an individual), as a legal entity (if we are a company) and many more, depending on the actions we need to carry out online.
In this post we will help you to find out about the different types of digital certificate and the most common uses of each of them so that you can choose the most suitable one according to your needs.
To establish a general division, we can classify the certificates according to 3 different actions: if we want to carry out transactions with the Public Administrations, Business transactions or more technical things related to Components.
There are three types of certificates for dealing with public administrations, either as a public employee or as an external person, which are suitable for each situation:
If we need that an employee uses the digital certificate to carry out a procedure on behalf of the company, we must think about the figure of that person and their relationship with the company when choosing between one type of certificate or another. Thus, we have:
These digital certificates differ from the certificates seen until now, since they do not serve to identify people when they carry out an online transaction, but rather to complement, protect and secure IT processes.
Do you need to deal with the Public Administration or sign a digital contract with a supplier? Whatever your situation, you already know the different types of digital certificate and you are ready to choose the most suitable one for each situation!
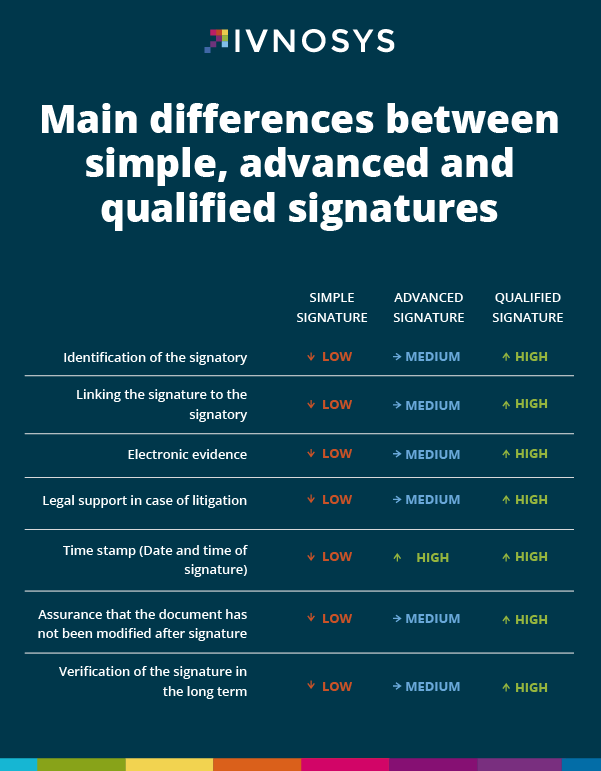
How many digital signatures are there? What level of security do I need depending on my activity? What does a qualified signature consist of? Every day we receive thousands of queries about which type of signature is most suitable for each company depending on the level of legal and juridical protection required or desired in their internal and external management.
Today we tell you in a very visual and simple way the 3 types of signature recognised by the eIDAS regulation and the degree of security offered by each of them.
The eIDAS regulation (EU) 910/2014 regulates electronic transactions and communications, establishing the 3 types of electronic signature accepted by all European Union countries: simple signature, advanced signature and qualified signature.
As stated in article 3 of the eIDAS regulation, an electronic signature refers to “data in electronic form that is unrelated or logically associated with other electronic data and is used by the signatory to sign”.
Thus, there are 2 key elements to be taken into account in electronic signature:
As we mentioned, one of the benefits of using electronic signature is that it allows you to sign documents and carry out all kinds of transactions with full legal validity within the EU. Let us now see what types of electronic signature are suitable for us depending on the situation we are in and the activity of our company.
The signatory accepts or rejects the information received by responding to an on-screen dialogue box, which is generally based on an “Accept/Reject” of the document sent. In other words, it does not require a trace as such, but only a click is enough to show the conformity of the information.
This is the easiest type of electronic signature for the signatory, as it does not require additional technology and allows to accept an agreement quickly and easily. However, it is the least legally robust type of electronic signature, as the identity of the signatory cannot be indisputably assured.
For this reason, the simple signature is valid for very basic day-to-day communications such as changes in the privacy policy or communications to employees that do not require a high level of security on the part of the company.
The advanced electronic signature has a higher level of security than the simple signature. According to article 26 of eIDAS, in order to have an advanced signature, the following requirements must be complied with:
a) be uniquely linked to the signatory
b) allow identification of the signatory
c) created using electronic signature creation data that the signatory can use, with a high level of confidence, under his exclusive control, and
d) be linked to the data signed by it in such a way that any subsequent modification of the data is detectable
The advanced electronic signature can be used by 2 methods:
The signatory receives a code by SMS – valid for a period of time and for one-time use only – which must be entered at the time of signing. This type of electronic signature is very common when making online purchases or signing contracts in the recruitment process.
In this case, the signatory’s identity is guaranteed by the use of a personal element at the time of signing: his or her mobile phone.
This electronic signature requires the physical presence of the signatory, as he/she needs to sign on a specific tool (usually a tablet). Biometric data is collected that identifies the signatory, such as the pressure, inclination and position of the pen used at the time of signing.
This type of electronic signature is commonly used in sectors such as banking and insurance, as it allows them to speed up the closing of transactions in person.
The qualified signature is the most legally robust type of signature that provides greater security in the event of a dispute. It must meet three essential requirements:
The digital certificate is defined as “an digital signature certificate that has been issued by a Qualified Trust Service Provider“. The certificate must be issued by a Certification Authority, an officially recognised entity that endorses the signatory’s identity.
At Ivnosys we have the IvCert electronic signature platform, making available to our customers all types of electronic signatures recognised by eIDAS. The tool allows the signing and sending of documents, collecting them signed in minutes and with full legal certainty.
In addition, Ivnosys is recognised as a Qualified Trust Service Provider and Certification Authority, complying with the security standards of its signature and digital identity solutions.
In recent months, companies have been forced to digitise their processes as a result of the pandemic. This change has been reflected, among other areas, in HR. Until then, recruitment and other employment procedures were carried out face-to-face. However, this way of working has been interrupted and, for the time being, there is no end.
Faced with this situation, professionals have seen an opportunity in digital signature as it allows them to speed up contracting processes, optimising their time and ensuring that the signed documents are fully legally valid.
 Technology offers the possibility of automating the work of professionals in charge of labour relations with their employees. In the case of the digital signature, it is an opportunity to optimise their work, reducing the time spent on administrative tasks with little value and focusing their efforts on issues that really require it.
Technology offers the possibility of automating the work of professionals in charge of labour relations with their employees. In the case of the digital signature, it is an opportunity to optimise their work, reducing the time spent on administrative tasks with little value and focusing their efforts on issues that really require it.
This is the case, for example, in recruitment processes. With the digital signature we offer the candidate the convenience of signing documents at any time, and from any device. This will increase their level of satisfaction with the company and their commitment to it. Thus, we must not forget that the differentiation of a company is promoted, among other factors, by the ability to attract and retain talent.
In companies, a multitude of employee-related tasks are performed daily, which in many cases require the signing of documents. Having an electronic signature makes it possible to optimise these tasks throughout the employee’s life cycle. That is, from the moment an employee is hired until the end of his or her activity in the company.
 As we have seen, digital signatures have many advantages for HR professionals. These are the main reasons why a company needs to digitise the relationship with its employees:
As we have seen, digital signatures have many advantages for HR professionals. These are the main reasons why a company needs to digitise the relationship with its employees:
Following the technological irruption in the business world in 2020, numerous digital tools have been implemented in companies at a vertiginous rhythm. This is why we are sometimes unfamiliar with the platforms we work with. In the case of electronic signatures, we know that there are different types, but it is increasingly common to hear this question: What is the most secure signature with the greatest legal guarantee?
The European eIDAS regulation recognises 3 types of electronic signature: the simple, advanced and qualified signature. All are valid, legally binding and admissible in court, but we must bear in mind that their legal strength is different, with the lowest being the simple signature and the strongest being the qualified one, which is equivalent to the traditional handwritten signature for legal purposes.
There are certain cases, in which either because it is convenient to have maximum legal security, or because the legislation itself obliges us to use an electronic signature equivalent to the handwritten one, we will opt for the qualified signature. Therefore, we will focus on the qualified electronic signature, due to the benefits it provides in terms of security and legal validity.
The qualified electronic signature is based on the use of qualified digital certificates and the generation of the signature using a secure signature creation device known as QSCD (Qualified Signature Creation Device).
To be considered as a qualified eletronic signature, an electronic signature must also meet three requirements:
As we have already mentioned, the QSCD is a cryptographic device that must have a high level of security as the certificate must only be able to be used on this device (card, hardware security module or HSM, USB…). This device is responsible for generating qualified signatures through the use of specific hardware and software that guarantees that only the signatory has control of their private key in accordance with a Common Criteria EAL4+ certification, which is the security standard created for QSCD cryptographic modules.
In the case of IvSign, it allows the user to have qualified certificates issued directly in QSCD.
We assume that a digital certificate is like an electronic version of a passport or a driving licence. Therefore, the signature creation data must be backed by a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP) in order to remain unique, confidential and protected against fraud. In addition, a qualified certificate can only be acquired through a qualified Certificate Authority, which performs a rigorous verification of the signatory’s identity.
Ivnosys is a Certification Authority and has the proper capacity to issue and revoke certificates, verify and guarantee the identity of the holder and the uses made with the certificate. Once a certificate has been issued, the signatory is ready to sign documents online. The next step is to choose the programme or platform with which to sign the document.
Electronic signature offer numerous advantages: greater agility in closing contracts, signing from any device, saving paper, avoiding unnecessary visits, avoiding new sales opportunities, avoiding routine tasks of searching and filing documents, improving the company’s image, etc.
And there are even more advantages to be gained by using qualified electronic signature:
It is time to be close to those who need us most. In keeping with our social commitment, at Ivnosys we have donated our tools to the NGO Manos Unidas. Thus, the organisation is at the forefront of social organisations by implementing a project to digitise its processes.
The objective of this collaboration agreement is to provide Ivnosys services at zero cost, including a system for the centralisation of digital certificates, electronic signatures and the management of notifications issued by public entities. These tools will allow Manos Unidas to centralise, protect and manage the digital identity of the electronic transactions it carries out, as well as guaranteeing significant time and cost savings.
“Our organisation carries out development projects in almost 60 countries in Africa, America and Asia, as well as having a local presence in Spain through 72 delegations. In addition, to carry out our work, we collaborate with more than 300 public organizations and hundreds of private entities. This complexity and extension of our activity requires the most cutting-edge and efficient technological solutions in the sector, which is why the agreement with Ivnosys will be a key element in our digital transformation process”.
Clara Pardo, President of Manos Unidas
The platform of digital certificate centralisation, IvSign, will allow Manos Unidas to centralise all its certificates, donated by Camerfirma, in a single platform, which will make it possible to share the use of these certificates with the people who work in the most controlled and secure way. This system keeps track of who, when and what they access with digital certificates.
On the other hand, the IvNeos system will allow Manos Unidas to automatically synchronise the electronic notifications it receives from public administrations, which translates into the monitoring of notifications from 9,000 public bodies. These notifications will be received in a single mailbox and the same platform will allow the relevant responses to be sent.
“We are excited to partner with such an essential organisation as Manos Unidas and help them, where possible, to streamline and secure their work processes through digital innovation so that they can continue to carry out their development cooperation initiatives. These tools will become the new way of communicating with donors, suppliers and partners for the organisation”. Sergio Ruiz, CEO of Ivnosys

Finally, the use of the IvCert electronic signature platform is donated. This tool will facilitate the optimisation of processes such as the collection of permissions for the transfer of data, image rights or confirmation of aid delivery, as well as providing them with the maximum legal guarantee thanks to the collection of electronic evidence that protects the signed documents.
Thanks to IvCert, Manos Unidas will be able to sign and send its digital documents with the guarantees of the European eIDAS regulation. In addition, the organisation will be able to take advantage of this platform to respond to its internal procedures, making it easier to manage all transactions with suppliers, donors and employees.